21 October 2015
Jon Palfreman's new book: Brain Storms: The Race to Unlock the Mysteries of Parkinson’s Disease
The Journal of Parkinson’s Disease is proud to announce the publication of Media Editor Jon Palfreman’s newest book: “Brain Storms: The Race to Unlock the Mysteries of Parkinson’s Disease”, a long-overdue, riveting detective story of the race to stop or reverse neurodegenerative conditions like Parkinson's disease, and a passionate, insightful account into the lives of those affected.
24 June 2015
New Study Calls for Partnering of Parkinson’s Disease Research Community with Patient Groups to Improve Effectiveness of Clinical Trials
Despite an urgent need for new medications, clinical trials in Parkinson’s disease (PD) have a relatively low rate of success. The reasons for this are complex, prompting a group of investigators from PD advocacy groups to conduct a survey of the principle stakeholders, PD scientists, patients, and caregivers, to determine some of the underlying barriers. Their results are published in the Journal of Parkinson’s Disease.
24 June 2015
What Is the Role of the Gut Microbiome in Developing Parkinson’s Disease?
In recent years, an important Parkinson’s disease (PD) research focus has been on gut-related pathology, pathophysiology, and symptoms. Gastrointestinal dysfunction, in particular constipation, affects up to 80% of PD patients and idiopathic constipation is one of the strongest risk-factors for PD. Lifestyle factors such as smoking and coffee consumption, as well as blood urate levels, have been associated with a decreased PD risk.
26 February 2015
Levodopa-Carbidopa Intestinal Gel May Prove More Effective for Long-Term Treatment of Parkinson’s Disease than Standard Levodopa
Although levodopa remains the “gold standard” to effectively control motor deficits in the treatment of early stage Parkinson’s disease (PD), it loses effectiveness as the disease progresses. After four to six years of treatment with oral medications for Parkinson’s disease, about 40% of patients experience lack of muscle control (dyskinesias), end-of-dose wearing off, and fluctuations in “On/Off” states. By nine years of treatment, about 90% will suffer these effects.
25 February 2015
Parkinson’s Disease Patients Have Reduced Visual Contrast Acuity
Patients with Parkinson’s disease (PD) often have difficulties with visual acuity in low-contrast images. Because they may have normal high-contrast vision, this is often overlooked during routine eye exams. In the current issue of the Journal of Parkinson’s Disease, researchers report that PD patients had significantly worse vision for low-contrast images at close (40 cm) and far (2 m) distances. Even for high-contrast images, PD patients’ vision was deficient at far distances.
18 November 2014
Simple Clinical Tests Help Differentiate Parkinson’s Disease from Atypical Parkinsonism
Two simple tests conducted during the neurological exam can help clinicians differentiate between early-stage Parkinson’s disease (PD) and atypical parkinsonism. By asking patients to perform a tandem gait test and inquiring whether they are still able to ride a bicycle, clinicians can ascertain whether medio-lateral balance is impaired, a defining characteristic of atypical parkinsonism. These findings are published in the Journal of Parkinson’s Disease.
11 September 2014
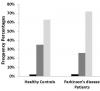
Few Mild-to-Moderate PD Patients Suffer from Malnutrition, Yet Almost One Third Are at Risk
Patients with Parkinson’s disease (PD) can experience difficulties with food preparation and ingestion, which could contribute to poor nutrition and place them at risk for malnourishment. Published studies have also suggested that PD is associated with low weight, however, few studies included control groups. A report published in the Journal of Parkinson’s Disease counters this conclusion in patients with mild-to-moderate PD, finding that the incidence or risk of malnutrition is no different for patients with mild-to-moderate PD compared to healthy controls.
9 July 2014
Sleep Disturbances, Common in Parkinson’s Disease, Can Be Early Indicator of Disease Onset
Up to 70% of Parkinson’s disease (PD) patients experience sleep problems that negatively impact their quality of life. Some patients have disturbed sleep/wake patterns such as difficulty falling asleep or staying asleep, while other patients may be subject to sudden and involuntary daytime sleep “attacks.” In the extreme, PD patients may exhibit REM-sleep behavior disorder (RBD), characterized by vivid, violent dreams or dream re-enactment, even before motor symptoms appear. A review in the Journal of Parkinson’s Disease discusses the underlying causes of sleep problems in PD, as well as medications, disease pathology, and comorbidities, and describes the most appropriate diagnostic tools and treatment options.
24 June 2014
Deep Brain Stimulation Improves Non Motor Symptoms in Parkinson’s Disease as well as Motor Symptoms
Deep brain stimulation (DBS) has become a well-recognized non- pharmacologic treatment that improves motor symptoms of patients with early and advanced Parkinson’s disease. Evidence now indicates that DBS can decrease the number and severity of non motor symptoms of patients with Parkinson’s disease (PD) as well, according to a review published in the Journal of Parkinson’s Disease.
13 May 2014
Exenatide Has Potential as a Disease Modifying Agent in Parkinson’s Disease
A follow-up study of patients with Parkinson’s disease (PD) who participated in an earlier “proof of concept” clinical trial using exenatide showed that improvements persisted twelve months after discontinuing exenatide therapy. These data provide strong encouragement for the further study of this drug in patients with PD, report researchers in the Journal of Parkinson’s Disease.